Droplet activation, separation, and compositional analysis:laboratory studies and atmospheric measurements
N. Hiranuma1
, M. Kohn2
, M. S. Pekour1
, D. A. Nelson1
, J. E. Shilling1
, and D. J. Cziczo1,*
1Atmospheric Sciences and Global Change Division, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 902 Battelle Blvd., Richland,
Washington, USA
Institute for Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences, Goethe-University Frankfurt am Main, Frankfurt, Germany
*now at: Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Ave.,
Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA
Received: 1 December 2010 – Published in Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss.: 24 January 2011
Revised: 29 June 2011 – Accepted: 6 October 2011 – Published: 26 October 2011
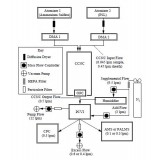
Abstract. Droplets produced in a cloud condensation nuclei chamber (CCNC) as a function of supersaturation have been
separated from unactivated aerosol particles using counter-flow virtual impaction. Residual material after droplets
were evaporated was chemically analyzed with an Aerodyne Aerosol Mass Spectrometer (AMS) and the Particle Analysis
by Laser Mass Spectrometry (PALMS) instrument. Experiments were initially conducted to verify activation conditions
for monodisperse ammonium sulfate particles and to determine the resulting droplet size distribution as a function
of supersaturation. Based on the observed droplet size, the counterflow virtual impactor cut-size was set to differentiate
droplets from unactivated interstitial particles. Validation experiments were then performed to verify that only droplets
with sufficient size passed through the counterflow virtual impactor for subsequent analysis. A two-component external
mixture of monodisperse particles was also exposed to a supersaturation which would activate one of the types (hygroscopic
salts) but not the other (polystyrene latex spheres or adipic acid). The mass spectrum observed after separation
indicated only the former, validating separation of droplets from unactivated particles. Results from ambient measurements
using this technique and AMS analysis were inconclusive,showing little chemical differentiation between ambient
aerosol and activated droplet residuals, largely due to low signal levels. When employing as single particle mass spectrometer
for compositional analysis, however, we observedenhancement of sulfate in droplet residuals.